When I look at software development from the Agile point of view, I perceive two types of work. One is what Agile calls a user story, and the other, for lack of a better term, let me call, building block.
All of us who have had any truck with Agile, have run up against these two types of work.
Further, many of us are stumped by these questions below.
How to distinguish between the two types of work? “Is this a user story, could that be a user story, shouldn’t this be a user story”, is a familiar song.
If a task is not a user story, and yet it is a significant effort, how do we fit it into a plan of action whose purpose is to only implement user stories? In other words, how do I fit the second type of work, the ‘building block’, into an iteration, sprint, time box, or whatever your particular flavor of Agile calls it.
Should this be a user story?
One of the first principles of the Agile philosophy provides the answer.
If you have not delivered value to the end user, you have not done the job. The driving focus of the Agile way is delivery to the end user, of a feature that she requires, asked for, and can recognize as such.
To illustrate, let us consider two different kinds of projects.
Auto Insurance Policy Administration System
You are building a policy administration system that can manage Auto Insurance policies.
Consider these tasks.
User Story
As a customer service rep, I want to query the DMV for a driver’s motor vehicle report.
This is a business function, expressed strictly in terminology that comes from the business user’s world. When you build this completely, from UI to backend, you will have a full vertical slice of business functionality, which you can set aside. Now, you can change focus to another vertical slice of business functionality, perhaps, querying a vehicle owner’s credit score.
Business folks know the auto insurance business. They do not know software engineering. Business folks can only evaluate the value of the system you are building, in terms of the business functions it helps them perform.
Can I query for the Motor Vehicle Report? Check.
Can I query for the Credit Report? Check.
We can write the sweetest code imaginable, but unless we place these business features in the business users’ hands, our job is incomplete. Such features are user stories.
Building Block – One
Build a library of UI widgets, backed by Twitter Bootstrap, which allows entry of entities in our domain model, like postal addresses, a vehicle description, an accident report, and so on. You should just be able to refer to these widgets, as necessary, in various screens of the UI
Creating such a widget set requires considerable skill, and time. However what can a policy admin representative do with a UI widget kit, however sophisticated it is? Nothing. The policy rep wants to take a driver’s information over the phone, and prepare an insurance quote for the driver. That is a user story, which will be implemented using, among other things, the above UI widget set. Creating the widget set itself, is not a user story. The widget set is a ‘building block’.
Building Block – More
Build a fault tolerant API that can send any query to DMV. The API must tolerate connection failures up to a certain number of times, which must be configurable.
When we have built said API, does the business user have a feature that they can do business with? No. However, you can build the ability to request a Motor Vehicle Report, on top of this API. Only then do you have a tool that a business user can clearly identify as an essential cog of their business.
Here are some more tasks that are merely building blocks in the Policy Adminstration project.
You have to build a data access API that hides the details of your application’s datastore, MongoDB, from the rest of the application. In other words, this is one of the layers in your application.
Your application has to schedule various activities. So you create a simplified facade around some proprietary, and complex scheduler that your company just bought.
After several sprints of work, you decide that a critical API method (EnrollmentService.enroll, for instance), has become too unwieldy and must be refactored, as defined by Martin Fowler et al. However this is a high risk task, which will require significant skill, effort, and time.
To summarize, a project often has tasks which you require to reliably implement user stories. Completing such a building block puts you on the road to producing a business feature that users recognize, but it does not get you all the way there.
Re-engineer the enrollment, and billing sub-systems
Now, let us consider a different kind of project.
Your policy administration system was delivered and has been in use for over a year. Periodically, problems have arisen, but you have kept the system going through bug fixes, work arounds, cleaning up data directly, and so on. After a year or so, the code has become so baroque, that even bug fixes are becoming difficult to do. So you decide that two critical sub-systems, enrollment, and billing must be re-engineered. The UI cannot be touched. All features that the user has been using for a year now must stay intact. Any changes you make must be under the hood.
Can this project be planned, and executed in an Agile manner? How can we break up the work into user stories, when we are not adding any business features at all?
Agile is not so much about any one kind of project, as it is about how to drive a project to completion.
- Figure out the primary stakeholder that asked for the project
- Figure out how that stakeholder views the deliverables of the project.
- Slice up those deliverables into smaller goals (sometimes called user stories), such that the stakeholder is always able to unambiguously see, in terms that matter to him, what has been completed and what remains to be done.
- Pick a fixed interval (aka sprint) of no more than 2 or 3 weeks, within which you can start and completely finish one or more of the above user stories
- Prioritize, and schedule the user stories across the sprints
- Execute a sprint, examine how you did at the end of the sprint, adjust, and execute next sprint
I can see no reason why we cannot apply the above method to a purely technical project, like the one under consideration. Some technical lead will be responsible for defining what the problem is, and what success looks like. This technical lead should be able to break up the larger goal into smaller ones which are easily measurable.
Perhaps, the enrollment and billing subsystems consist of 3 interfaces, and 3 implementation classes. The interfaces must stay untouched. The 3 implementation classes must be refactored. Perhaps each class can be a ‘user story’.
If those ‘user stories’ turn out to be too big to fit into a sprint, we can break them up into individual interface methods. Perhaps each ‘user story’ is simply the re-engineering of a couple of interface methods.
Perhaps, the enrollment and billing subsystems support a dozen business use cases, and we know exactly which service methods support which use case. Perhaps we could break up the refactoring work according to these business use cases. Each user story consists of refactoring the service methods that support one of those dozen business use cases.
The larger point is that all projects have to be delivered. All projects have some stakeholder who knows what shape that delivery must take. Slices of that delivery are user stories. All other work that must happen in order to deliver those user stories in good order, are building blocks. In this refactoring project, say you want to write automated integration tests, which will ensure that user functionality has not been broken. This would be a ‘building block’. A whole class, refactored to our satisfaction, which passes those integration tests, would be a ‘user story’.
How to fit ‘building blocks’ into sprints?
If the ‘building blocks’ do not already exist, before you start the Agile project, let them be subsumed by the user story.
Say that first story, of the first sprint, is the Motor Vehicle Report query that we saw earlier.
As a customer service rep, I want to query the DMV for a driver’s motor vehicle report.
Building Block – One
Before you are able to start implementing the user story, you need a development environment, which might include a source control project, a build script, private DB schemas for each developer, a continuous integration server, and a test environment where the latest build can always be found.
Already available?
It is possible that much, if not all of this, is already available. You have established a development environment over time, and across previous projects. As part of the first user story, in the first sprint, simply do what little is required to setup your development environment for this particular project.
Starting from scratch?
Perhaps you have decided that from this project onwards, you are switching to Git for source control, and your build scripts will be in Gradle instead of the Maven that you used previously.
As part of the first user story, you prepare your Git repositories, and write whatever Gradle script is required to get you through the first user story. Since this is new, you will spend more time on this, than you would have, if you had stuck with the previous technologies. That is fine. It simply means that it will take longer to complete that same first user story.
Is this Greek to you?
You have never written a build script before. You have never used ANT, nor Maven, and hence it will signficantly longer to learn the Gradle necessary for your build scripts.
This just means that it will take you even longer to complete that first user story, since it will take even longer to create your development environment.
Building blocks simply get factored into Velocity
The more time you spend getting your building blocks in place, the more time it takes to complete a user story. The faster you are able to complete your building blocks, the faster you will complete your user story. That is really all there is to it.
Many factors determine how much time you will spend on the building blocks. Do you already have them built, before starting the user story? Are you accomplished at designing and building the particular building block in question, which means you can get through it quickly?
After using Agile in some form or the other for over 10 years, not always rigorously, nor effectively, I finally took a class on Scrum a couple of weeks ago. It was taught by Mike Cohn, of Mountain Goat Software, one of the earliest practitioners of Scrum for software development, and a prominent proponent of the methodology.
As you might imagine, folks brought up the questions we have been considering. Here are a couple of slides from the class, which speak to the matter.
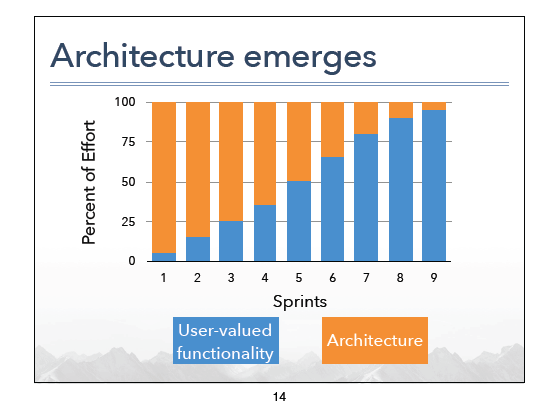
Mike Cohn used the term ‘Architecture’ to refer to what I have been calling ‘building blocks’. Mike posited that you do not want to think of ‘Architecture’ as separate from ‘user stories’. Consider ‘Architecture’ an intrinsic part of ‘user stories’. You will typically spend more time on ‘Architecture’ (my ‘building blocks’) earlier in a sprint, and in the earlier sprints. As you move through the project, if you are doing your engineering right, you will simply use already built pieces, or simply apply previously made design decisions, more and more.
As the above image shows, how good you are at getting the building blocks out the way, affects how much ‘user story’ you complete in a sprint, which in a word, is Velocity.
Look to the first principles
All through the four days of Scrum training with Mountain Goat Software, I heard question, after question, which would prompt the same thought in me. Just look to the first principles of Agile. The answers are there.
Of course, the challenge, for them and for me, is knowing those first principles.